Dengue
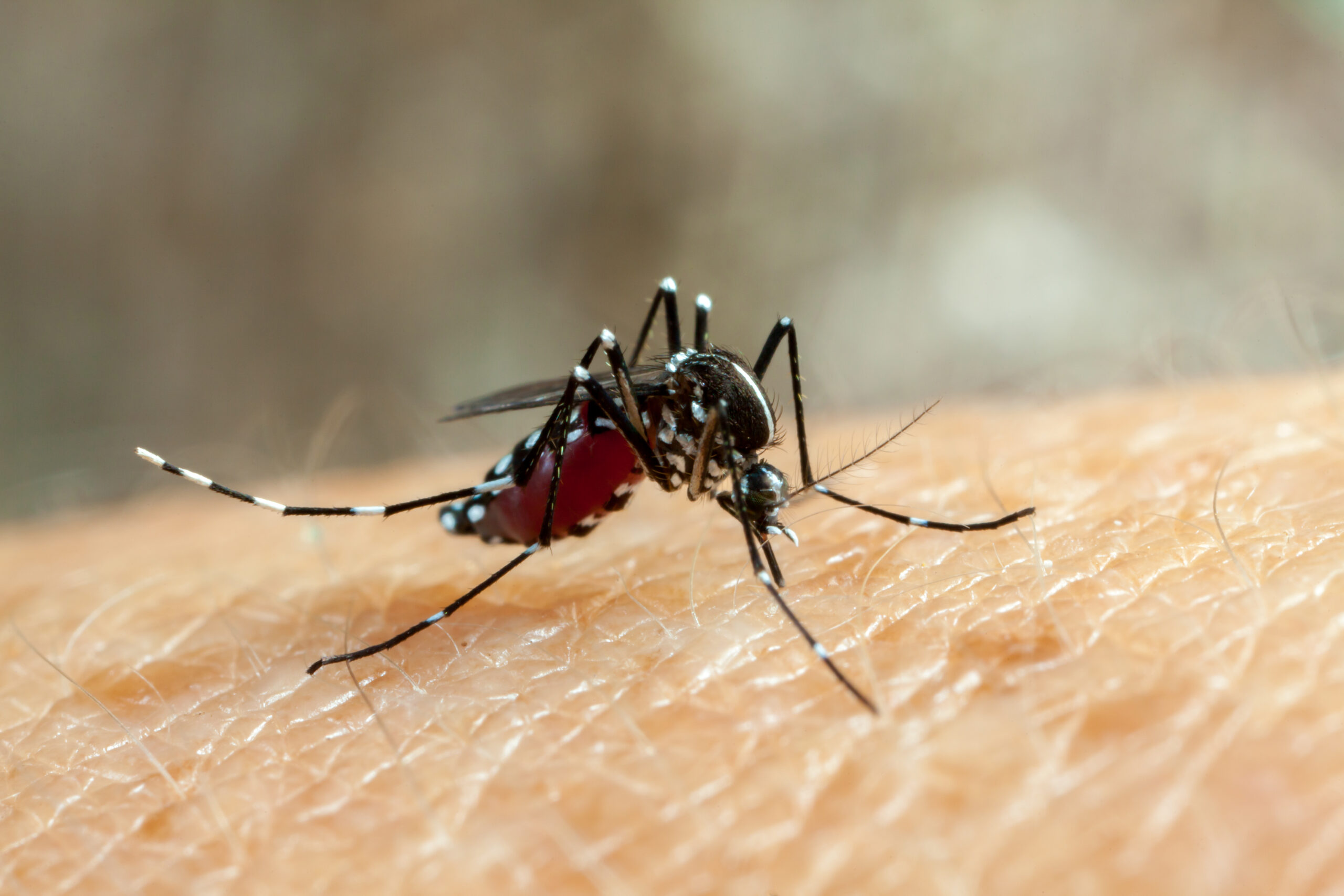
Dengue (pronounced DENgee) fever is a painful, debilitating mosquito-borne disease caused by any one of four closely related dengue viruses. Dengue fever is transmitted by the bite of an Aedes mosquito infected with a
dengue virus. The mosquito becomes infected when it bites a person with dengue virus in their blood. It can’t be spread directly from one person to another person.
Symptoms of Dengue Fever
Symptoms, which usually begin four to six days after infection and last for up to 10 days, may include
- Sudden, high fever
- Severe headaches
- Pain behind the eyes
- Severe joint and muscle pain
- Fatigue
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Skin rash, which appears two to five days after the onset of fever
- Mild bleeding (such a nose bleed, bleeding gums, or easy bruising)
People with weakened immune systems as well as those with a second or subsequent dengue infection are believed to be at greater risk for developing dengue hemorrhagic fever.
Treatment for Dengue Fever
There is no specific medicine to treat dengue infection. If you think you may have dengue fever, you should use pain relievers. You should also rest, drink plenty of fluids, and see your doctor. If you start to feel worse in the first 24 hours after your fever goes down, you should get to a hospital immediately to be checked for complications.
Preventing Dengue Fever
The best way to prevent the disease is to prevent bites by infected mosquitoes, particularly if you are living in or traveling to a tropical area. This involves protecting yourself and making efforts to keep the mosquito population down.
To protect yourself:
Use mosquito repellents, even indoors.
When outdoors, wear long-sleeved shirts and long pants tucked into socks.
When indoors, use air conditioning if available.
Make sure window and door screens are secure and free of holes. If sleeping areas are not screened or air conditioned, use mosquito nets.
If you have symptoms of dengue, speak to your doctor.
If someone in your home gets dengue fever, be especially vigilant about efforts to protect yourself and other family members from mosquitoes. Mosquitoes that bite the infected family member could spread the infection to others in your home.